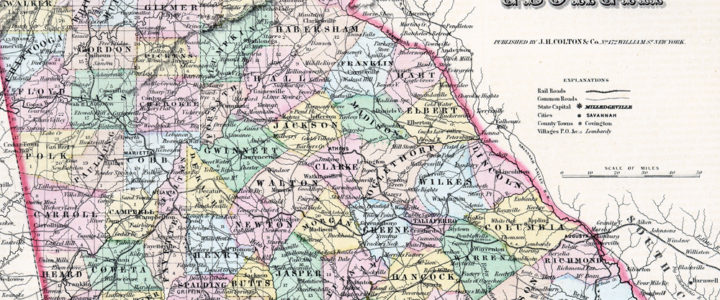
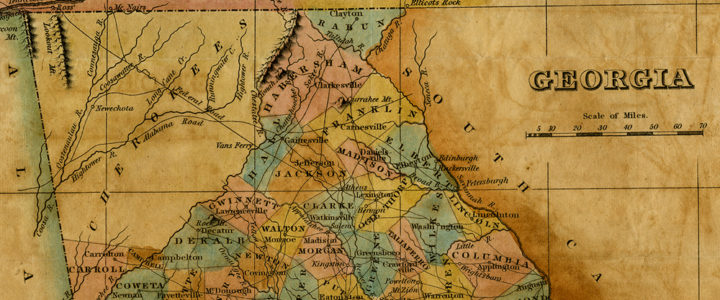
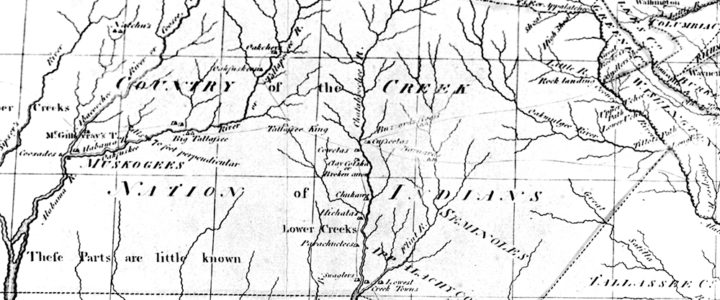
This map of Georgia was published in Colton’s Atlas of the World in 1856. The map shows Georgia’s westward expansion in the years following the forced removal of the Creek and Cherokee Indians from Georgia to reservations in modern-day Oklahoma. The map also shows the state’s railroads and common roads.
Map of Georgia, 1855. From the Georgia Historical Society Map Collection, MS 1361-MP 083.
View the description of this item in the GHS Library and Archives catalog.